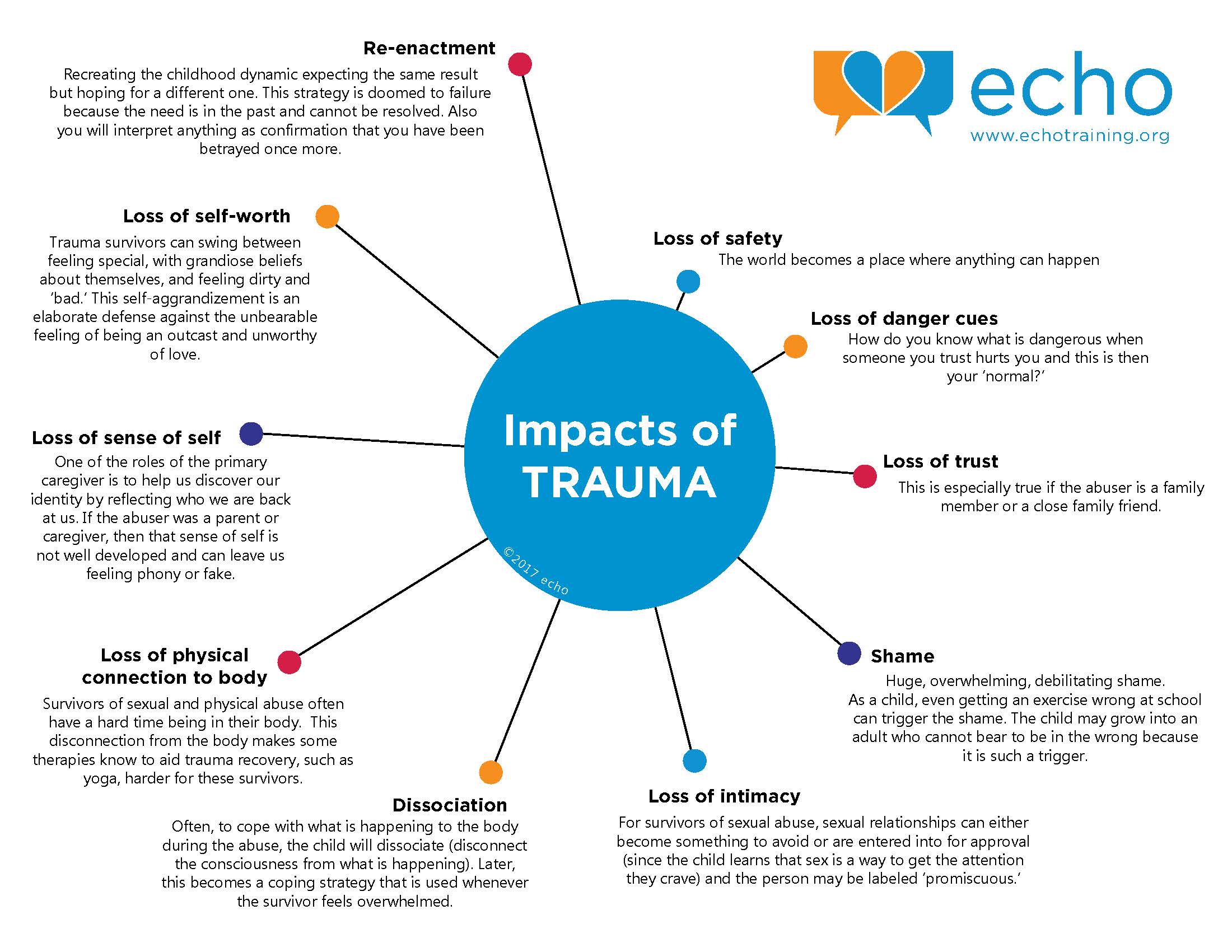
What would we do if we could see every psychological wound ever inflicted as a physical bruise? We would see a lot of black and blue people walking around! We might also be more careful of each other, understanding the degree of suffering we each have endured.
One of the hardest things when you are in a relationship is that there is no trauma map to refer to and even as we get to know someone’s history and the things that activate past trauma, we are often bewildered or downright indignant when trauma rears its head and our loved ones lash out, retreat, get emotional for no understandable reason, or unfairly blame us for all kinds of wrongdoing.
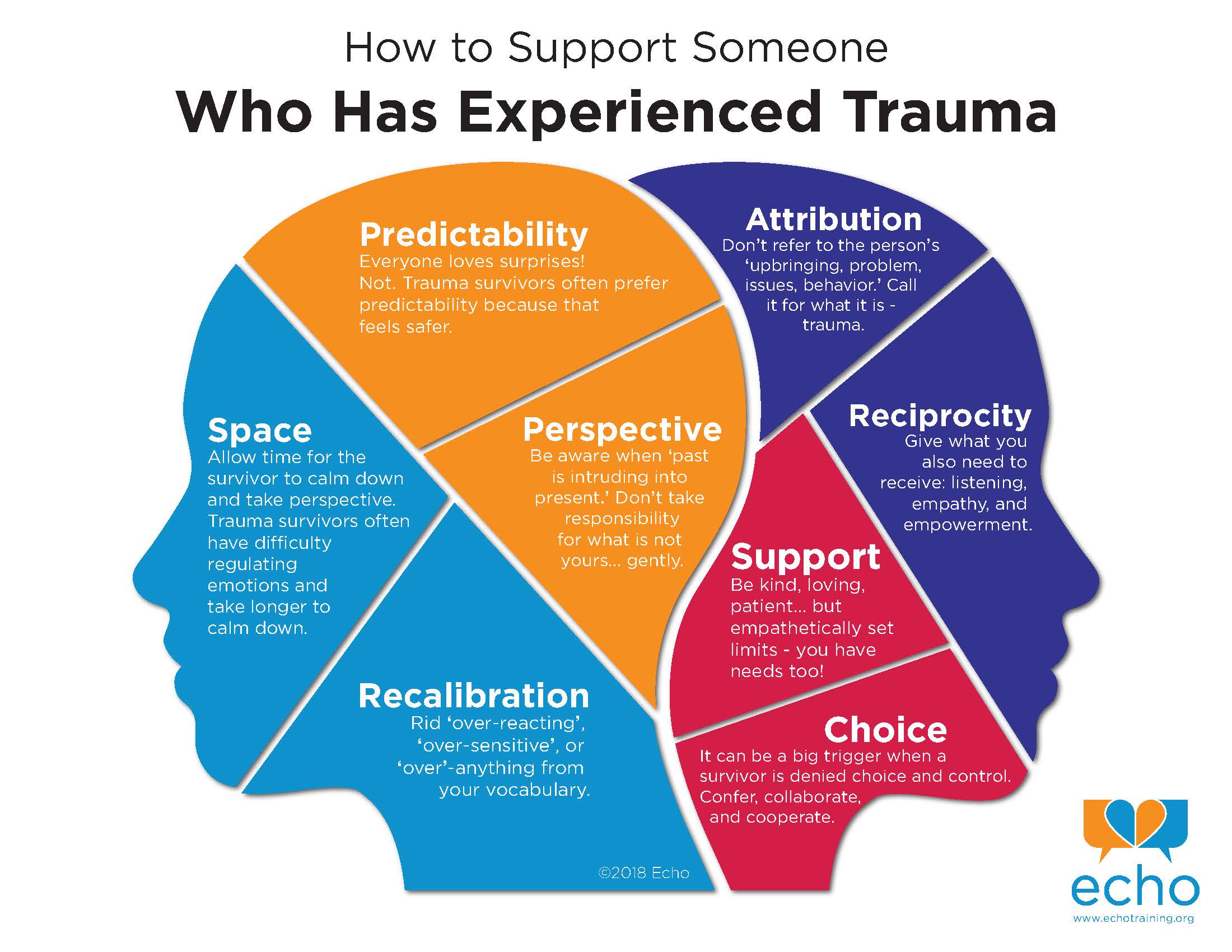
How do you negotiate these and other manifestations of trauma? We have put together a infographic based on relationship lessons learned by trauma survivors and those who love them.
- Predictability: Everyone loves surprises! Not. Trauma survivors often prefer predictability because that feels safer.
- Space: Allow time for the survivor to calm down and take perspective. Remember that we trauma survivors often have difficulty regulating our emotions and take longer to calm down. Maybe support self-soothing, for example suggesting you both go for a walk, maybe stay well clear! If the survivor is caught up in the fight/flight response you may be mistaken for the enemy.
- Perspective: Be aware when ‘the past is intruding into the present.’ Don’t take responsibility for what is not yours… gently. You can own any insensitivity or lack of consideration that has provoked the reaction and yet separate it from whatever past trauma is fueling what would otherwise appear to be a disproportionate response. Remember there is no such thing as ‘over-reacting’ – the reaction is in direct proportion to the pain experienced in the past rather than in response to what’s happening now.
- Rid ‘over-reacting,’ ‘over-sensitive,’ ‘over’-anything from your vocabulary.
- Language: Don’t refer to ‘your upbringing, your problem, issues, behavior.’ This sounds like judgment or at the very least like the trauma survivor is somehow broken or the problem. Call it for what it is – trauma.
- Be kind, loving, patient… But empathetically set limits – you have needs too! It’s okay to talk about when the survivor’s reactions hurt you too. “I love you and I understand how scared/angry/sad you are… and it’s not okay to hurt me.” Whatever our trauma history, we must all learn to be accountable when we hurt others.
- Reciprocity: Most of us had parents who lacked skills in listening, empathy, tolerating uncomfortable feelings, empowerment… Give what you also need to receive [because that’s the best way of making sure you get it back. Make sure that you are getting these things somewhere in your life. If the survivor is your friend or romantic partner, be sure that there is a two-way street. However much you love someone who has experienced trauma, it is unhealthy if you become a savior, therapist, or martyr.
- Control and choice. Big trigger when a survivor is denied these. Confer, collaborate cooperate. Unilateral moves even when benevolent will not be appreciated! Trauma is about getting hurt when you had no power or control over the situation, and it is immensely activating when the trauma survivor experiences that powerlessness again. If you want one way to ensure one of the fight/flight/freeze/collapse survival responses, taking away control is the way to do it!